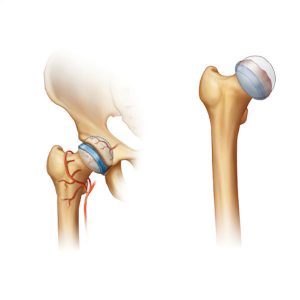
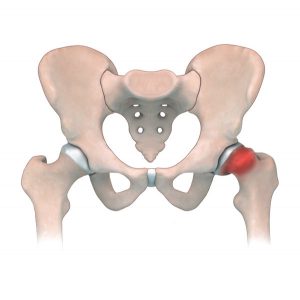
Articulated Hip Distraction along with a small diameter decompression (to help create new vascular channels to the femoral head) is a procedure which addresses many treatment principles for LCPD and in some cases, Hip Chondrolysis. The main principles of treatment include maintaining motion of the hip and containing the femoral head inside the acetabulum. If the femoral head stays insides the acetabulum, then it will re-shape over time and stay rounder. If the hip starts to come out of the socket (subluxation) it will more likely deform and stay deformed thereby causing pain and premature arthritis (wear and tear) later in life.
Indications / Candidacy
Articulated hip distraction is used to treat Legg-Calvé Perthes disease (LCPD), which usually affects children between the ages of 6-10. In patients that have this condition, the femoral head (hip) loses its blood supply and then slowly re-vascularizes over the next 2-4 years. As the hip dies, the femoral head collapses causing stiffness and contractures of the muscles around the hip which can lead to subluxation. Articulated Hip Distraction may also be among the treatment considerations for Hip Chondrolysis. This condition usually affects adolescents, in which there is progressive and rapid destruction of the cartilage in the hip joint.
Good candidates for this surgery have:
- Legg-Calvé Perthes disease (LCPD) presenting with subluxation of the hip
- Juvenile avascular necrosis (AVN)
- Hip Chondrolysis


Treated Conditions
The Canadian Limb Lengthening Center offers a team of experienced surgeons, nurses and physiotherapists that make patients feel supported throughout their entire treatment process. Our ability to treat complex orthopedic conditions with a holistic approach gives our patients the best possible outcomes. We pride ourselves in providing highly specialized, expert care that helps patients and families dealing with Perthes disease, among many other diseases. To learn more about conditions treated with Articulated Hip Distraction, follow the links below:
Surgical Technique
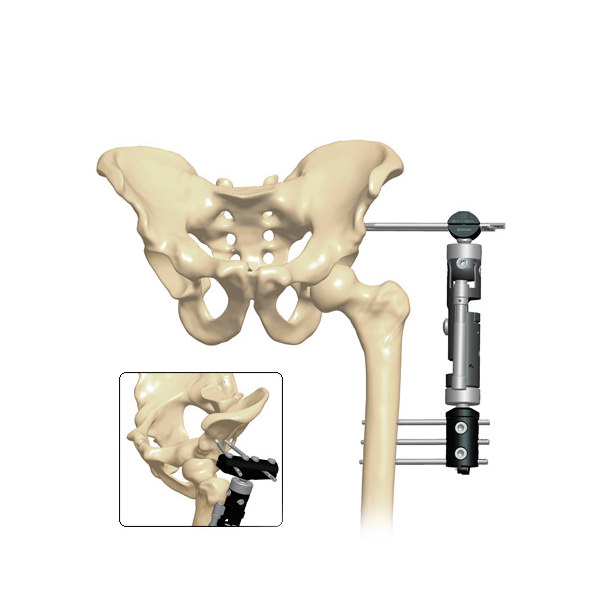
During Articulated Hip Distraction the articulated external fixator is used to help reposition the femur in the hip joint (a process called containment). It is articulated to maintain hip motion thereby allowing synovial circulation (which helps heal the cartilage). The external fixator is then used to gradual distract the femur from the acetabulum to minimize mechanical stresses on the hip joint. This prevents further collapse and allows the femoral head to re-grow.
- The patient is placed on the table in a supine position (on their back).
- The affected side is placed at the edge of a radiolucent table, and the affected leg is positioned in abduction and extension on a padded stand.
- A skin incision is performed in order to release the adductors. If the patient has a fixed hip flexion contracture, the patient undergoes an anterior release as well.
- A 1.5mm wire is inserted up the femoral neck and into the center of the avascular lesion in order to perform a small diameter core decompression of the necrotic zone of the femoral head.
- A cannulated 3.2-mm drill is used to create a small-diameter bone channel into the necrotic bone.
- Following this, a hip arthrogram is performed. (A liquid dye placed into the hip to allow visualisation of the cartilage of the femoral head.)
- The affected leg is then placed into full extension and at least 25 to 30 degrees of abduction. Containment of the femoral head is confirmed on fluoroscopy.
- An articulated rail type external fixation system is then applied to the hip in this position. When the frame application is complete, the hinge point is verified by flexing and extending the hip joint under fluoroscopy. The hip joint is acutely distracted 3 to 5 mm.
- Patient is then returned to the recovery room.
Results
Articulated Hip Distraction as treatment for LCPD heavily aims to achieve a round or spherical femoral head that “fits” into the hip cup. Hip distraction in Perthes’ disease unloads the joint, which negates the harmful effect of stresses on the articular surfaces. Younger patients have a better chance of a successful outcome because the more growth the child has remaining, the more remodeling/healing can occur of the femoral head. For many patients this means providing adequate function and hip range of motion. It also means less complications, pain and discomfort later in life.
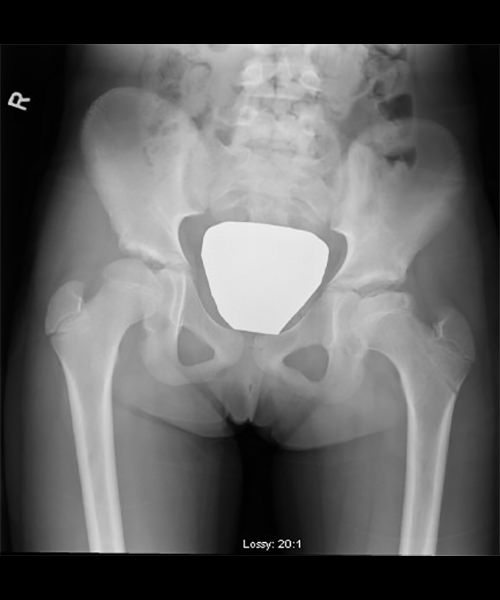
Pre-op
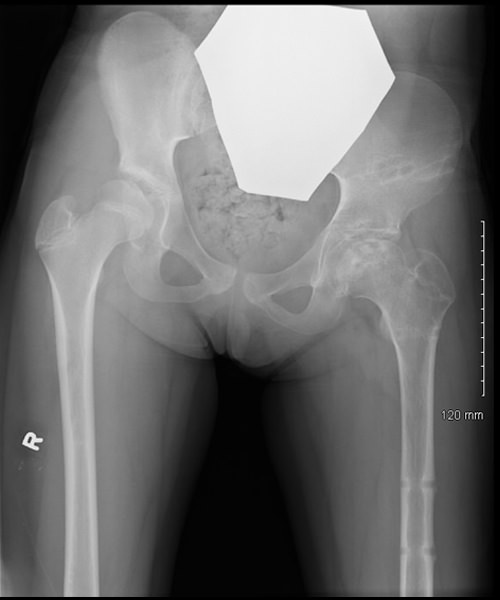
6 weeks post op
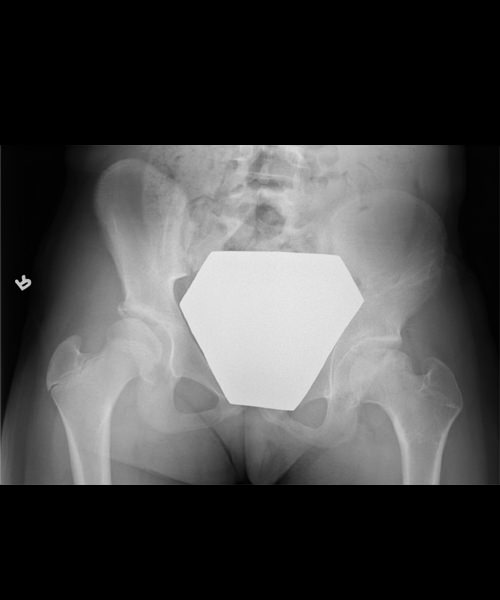
6 months post op
Potential Complications
As with any surgical procedure, Articulated hip distraction can have difficulties and complications. In most cases, our team of specialist can address these concerns without compromising the end results or outcome. Complications and side effects may include:
- Loss of hip joint mobility and strength
- Fracture of femur or hip
- Nerve injury to the sciatic nerve (Neuropraxia)
- Infection of bone (osteomyelitis)
- Neurovascular injury or stretch (very rare)
Case studies
AM I A CANDIDATE?
Are you experiencing an orthopedic condition and would like to improve your physical capabilities?
Or you simply would like to achieve your long-lasting dream of improving your height?
Let us help you achieve your optimal health and wellness in a professional setting.
Let’s open up a discussion to help you achieve your goals.




Highly specialized expert care at CLLC
At the Canadian Limb Lengthening Centre we offer complex deformity correction and limb lengthening surgeries performed by experienced surgeons with the most up to date technologies. When it comes to your care, and treatment of deformity and limb length discrepancy, our surgeons have extensive training and experience.